Score: 0 / 0
The Triplet Code
Each amino acid is encoded by a sequence of three nucleotides in the mRNA,
known as a
codon. Multiple
codons can code for the same
amino acid, which is a key feature of
the genetic code.
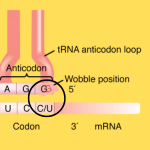
Wobble base pairing allows for some
flexibility in the third position of the codon, enabling a single tRNA
to recognize multiple codons that code for the same amino acid.
 Missense mutations change one amino
acid in the protein sequence, while
silent mutations do not change the amino
acid sequence due to redundancy in the genetic code.
Nonsense mutations introduce a
premature stop codon, leading to a truncated protein.
Missense mutations change one amino
acid in the protein sequence, while
silent mutations do not change the amino
acid sequence due to redundancy in the genetic code.
Nonsense mutations introduce a
premature stop codon, leading to a truncated protein.
Dive deeper: AUG is the start codon, coding for methionine. UAA, UAG, and UGA are stop codons that signal termination of translation. The genetic code is nearly universal across all organisms, with some exceptions in mitochondria of the cell and certain protozoa.

